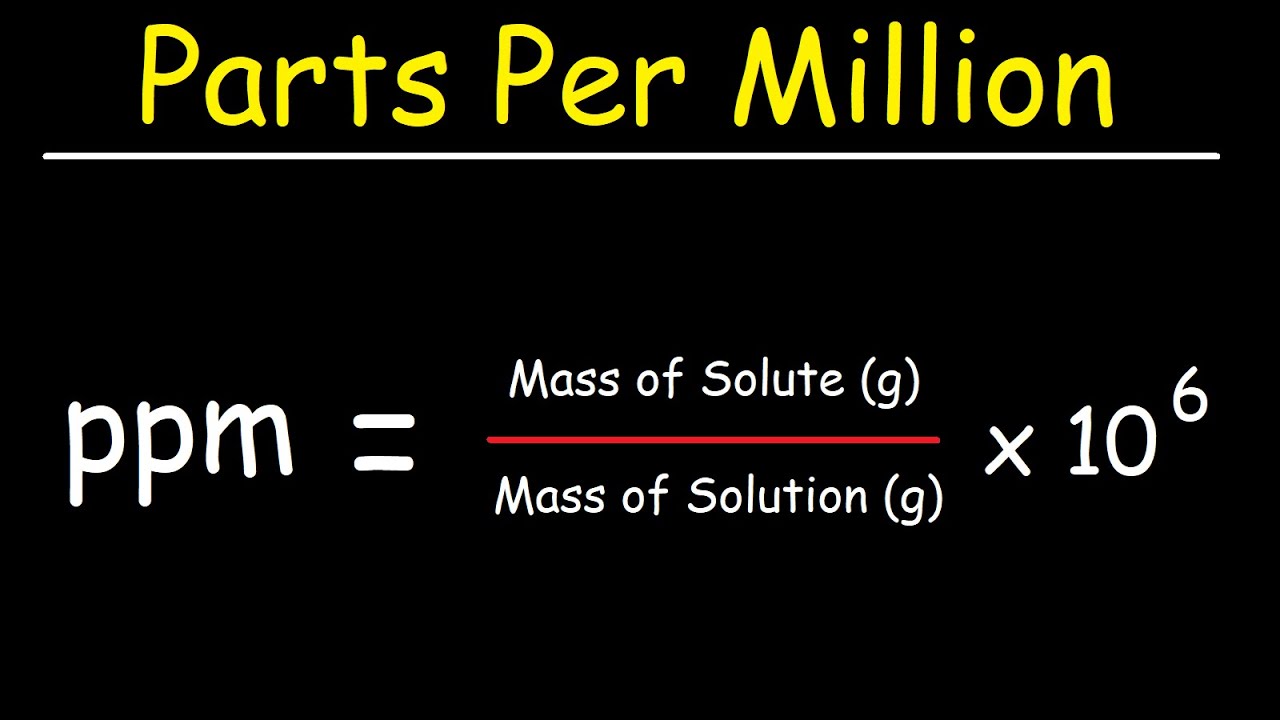PPM meaning is a term that holds significant importance across various industries, particularly in project management, finance, and engineering. As professionals and organizations strive for efficiency and effectiveness, understanding PPM becomes crucial. In this article, we will delve into the various interpretations of PPM, explore its applications, and provide insights that can enhance your understanding and practical usage of this term.
Throughout our discussion, we will break down PPM into its different contexts, from project management to parts per million in scientific measurements. By the end of this article, you will have a well-rounded grasp of PPM meaning and how it impacts different sectors.
We will also address common misconceptions about PPM, its relevance in today’s fast-paced world, and provide practical examples and statistics to reinforce the information presented. Whether you're a student, a professional, or simply curious about PPM, this guide will serve as a valuable resource.
Table of Contents
- What is PPM?
- PPM in Project Management
- PPM in Finance
- PPM in Science
- Common Misconceptions About PPM
- The Importance of PPM
- Examples of PPM in Different Contexts
- Conclusion
What is PPM?
PPM stands for "Parts Per Million," a unit of measurement that expresses the concentration of one substance in a million parts of another. This measurement is extensively used in various fields, including chemistry, environmental science, and engineering.
In addition to its scientific meaning, PPM is also an acronym for "Project Portfolio Management," which refers to the centralized management of one or more project portfolios to achieve strategic objectives.
Understanding PPM in Different Contexts
To fully appreciate PPM, it’s essential to explore its meaning in these distinct contexts:
- Parts Per Million (PPM) in scientific contexts
- Project Portfolio Management (PPM) in business and project management
PPM in Project Management
In the realm of project management, PPM refers to the methodologies and tools used to manage a portfolio of projects. This includes assessing project performance, resource allocation, risk management, and aligning projects with organizational goals.
Key Components of Project Portfolio Management
- Strategic Alignment: Ensuring projects are aligned with the strategic objectives of the organization.
- Resource Management: Efficiently allocating resources across projects to maximize output.
- Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating risks associated with project execution.
- Performance Monitoring: Continuously assessing project performance against set benchmarks.
PPM in Finance
In finance, PPM can refer to a range of management practices related to financial portfolios. It involves the analysis and management of financial assets to optimize returns and mitigate risks.
Importance of PPM in Financial Management
Understanding PPM in finance is critical for:
- Investment Strategy: Developing strategies to optimize investment portfolios.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluating financial risks and making informed decisions.
- Performance Measurement: Monitoring the performance of financial assets over time.
PPM in Science
In scientific contexts, PPM is often used to measure the concentration of pollutants in air and water, as well as in various chemical solutions.
Applications of PPM in Environmental Science
- Measuring Air Quality: Determining the concentration of harmful gases in the atmosphere.
- Water Quality Testing: Assessing the levels of contaminants in drinking water.
- Food Safety: Monitoring pesticide residues in food products.
Common Misconceptions About PPM
Despite its widespread use, there are several misconceptions surrounding PPM. Some individuals believe PPM is only relevant in scientific contexts, while others may not understand the nuances of its application in project management.
It’s crucial to clarify these misconceptions for a better understanding of the term.
The Importance of PPM
Understanding PPM is vital for professionals across various fields. It facilitates better decision-making, enhances project execution, and ensures compliance with regulatory standards.
Furthermore, a solid grasp of PPM can lead to increased efficiency and effectiveness in both project management and scientific research.
Examples of PPM in Different Contexts
To illustrate the application of PPM, here are some practical examples:
- In project management, a company may use PPM to prioritize projects based on their alignment with strategic goals, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently.
- In environmental science, government agencies may measure pollutant levels in parts per million to ensure air and water quality standards are met.
Conclusion
In summary, PPM meaning encompasses various interpretations that are crucial across different industries. Whether in project management, finance, or science, understanding PPM can significantly enhance decision-making and operational efficiency.
We encourage you to leave your comments below, share this article with others, or explore more content on our site to deepen your knowledge about PPM and its applications.
Thank you for reading, and we hope to see you back here for more insightful articles!
Article Recommendations
- Most Prominent Foreheads A Global Comparison
- Unveiling The Secrets Of The Caseoh Zodiac Sign A Comprehensive Guide
- Misav Your Ultimate Guide To Understanding Its Significance And Impact