The DROP command in SQL is a powerful tool used to remove various database objects, including tables, databases, views, and indexes. Understanding how to use this command correctly is crucial for anyone working with SQL databases. In this article, we will delve deep into the DROP command, its syntax, and its implications, ensuring you have a thorough understanding of this essential SQL operation. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced database administrator, this guide aims to enhance your SQL skills and knowledge.
The DROP command is often misunderstood due to its irreversible nature; once an object is dropped, it cannot be recovered unless you have a backup. This characteristic elevates the importance of using this command with caution. Throughout this article, we will explore the various contexts in which the DROP command can be utilized and provide examples to illustrate its usage. By the end of this guide, you will be equipped with the expertise to use the DROP command safely and effectively.
Additionally, we will discuss best practices and alternatives to the DROP command, such as using TRUNCATE or DELETE, depending on your specific needs. We aim to provide you with authoritative insights and trustworthy information that you can rely on as you manage your SQL database. Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
- What is the DROP Command?
- Syntax of the DROP Command
- Types of DROP Commands
- Using the DROP TABLE Command
- Using the DROP DATABASE Command
- Best Practices for Using the DROP Command
- Common Mistakes to Avoid with DROP Command
- Conclusion
What is the DROP Command?
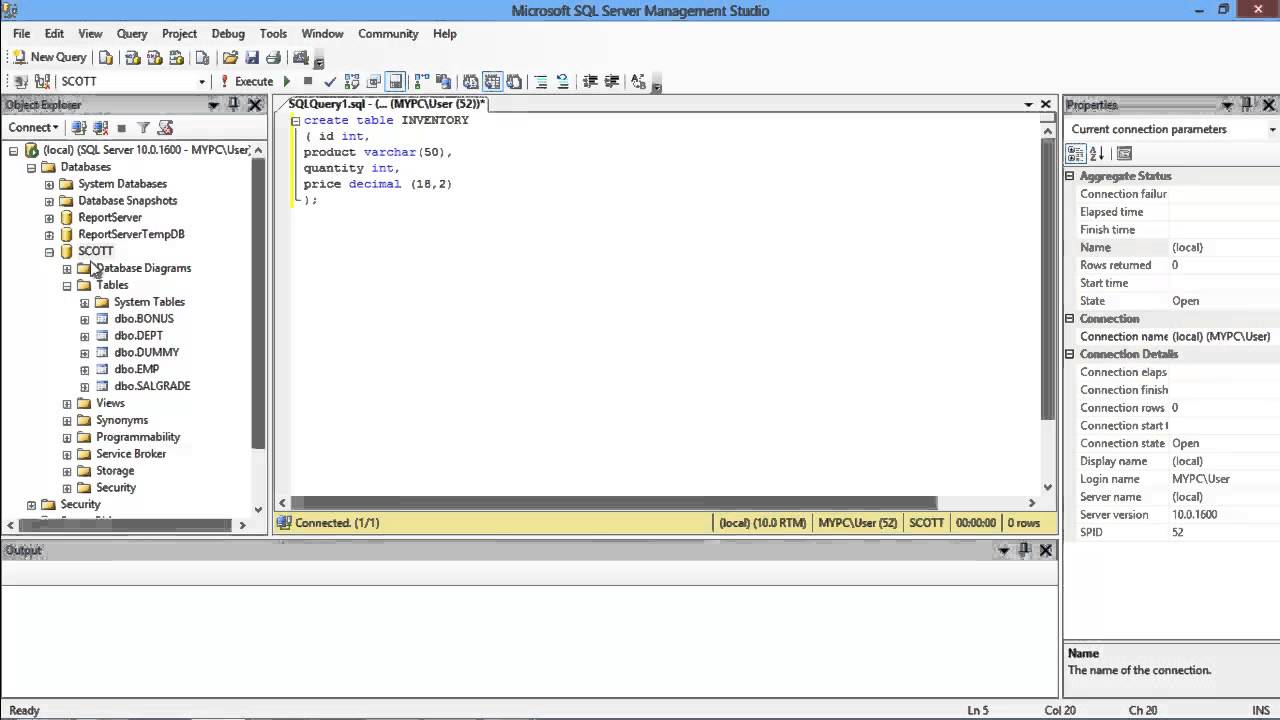
The DROP command in SQL is used to delete a database object permanently. This includes databases, tables, views, and indexes. When you execute a DROP command, the object and all of its data are removed from the database system completely. It is essential to note that dropping an object is irreversible, meaning that all data will be lost unless you have a backup.
Importance of the DROP Command
Understanding the DROP command is vital for database management. Here are a few key points regarding its importance:
- Efficient database management: Helps in maintaining and optimizing the database.
- Data integrity: Ensures that outdated or unnecessary objects do not clutter the database.
- Space management: Frees up storage space by removing large tables or databases that are no longer needed.
Syntax of the DROP Command
The syntax for the DROP command varies slightly depending on the type of object you wish to drop. Here are some common syntaxes:
Drop Table Syntax
DROP TABLE table_name;
Drop Database Syntax
DROP DATABASE database_name;
Drop View Syntax
DROP VIEW view_name;
Types of DROP Commands
There are several types of DROP commands that you can use depending on the object you want to remove:
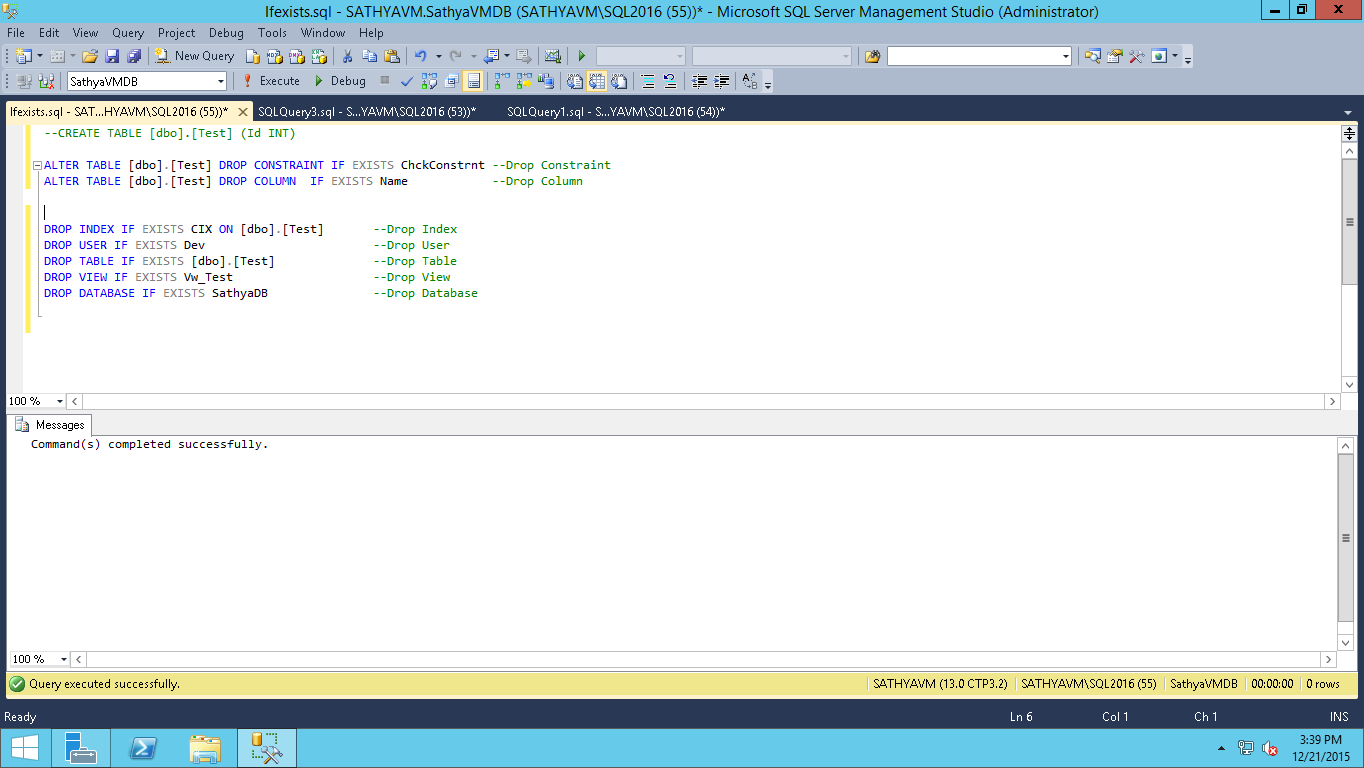
- DROP TABLE: Removes a table from the database.
- DROP DATABASE: Deletes an entire database along with all its tables and data.
- DROP VIEW: Removes a view from the database.
- DROP INDEX: Deletes an index from a table to improve performance.
Using the DROP TABLE Command
The DROP TABLE command is one of the most frequently used commands in SQL. Here’s how it works:
Example of DROP TABLE Command
DROP TABLE employees;
In this example, the command will remove the 'employees' table from the database permanently, along with all the data it contains.
Considerations Before Dropping a Table
Before executing a DROP TABLE command, consider the following:
- Ensure that you have a backup of the data if it is needed in the future.
- Check for any foreign key constraints that may prevent the table from being dropped.
- Consider using TRUNCATE if you only want to remove the data but keep the table structure.
Using the DROP DATABASE Command
The DROP DATABASE command is used to delete an entire database and all its contents. This command should be used with extreme caution due to its irreversible nature.
Example of DROP DATABASE Command
DROP DATABASE company_db;
This command will permanently remove the 'company_db' database and all the tables within it.
Precautions When Dropping a Database
Before executing the DROP DATABASE command, keep these precautions in mind:
- Always create backups of important data before dropping a database.
- Ensure that no active connections are using the database.
- Verify that the database is not required for any ongoing projects.
Best Practices for Using the DROP Command
To use the DROP command effectively and safely, consider the following best practices:
- Always back up your data before executing a DROP command.
- Use the command in a development or testing environment before applying it in production.
- Document your actions to maintain a record of changes made to the database.
- Restrict permissions for executing DROP commands to prevent accidental deletions.
Common Mistakes to Avoid with DROP Command
Here are some common mistakes to avoid when using the DROP command:
- Dropping objects without checking for dependencies, which can lead to broken relationships.
- Failing to create backups before executing the DROP command.
- Using the command in a production environment without proper testing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the DROP command is a powerful SQL operation that enables users to delete database objects permanently. Understanding its syntax, types, and best practices is essential for anyone working with SQL databases. Remember to always back up your data and use the command with caution to avoid unintended data loss. If you found this guide helpful, please leave a comment below, share it with others, or read more articles on our site for additional information.
Call to Action
If you have any questions or would like to share your experiences with the DROP command in SQL, please leave your thoughts in the comments section. Don’t forget to explore our other articles for more insights into SQL and database management!
Thank you for reading, and we hope to see you back here for more informative content!
Article Recommendations
- No Te Duermas Morena Video Viral The Phenomenon Gripping The Internet
- Rob Dyrdeks Ethnicity Exploring His Background
- Bisping Vs Rockhold 2 Ultimate Fight Preview