Normal QTc for women is a crucial aspect of cardiac health that often gets overlooked. It is essential to understand what QTc means, its significance in heart health, and how it varies between individuals, particularly women. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of QTc intervals, the factors affecting them, and the clinical implications of abnormal readings.
The QTc interval, or the corrected QT interval, is a measurement used in electrocardiograms (ECGs) to assess the time it takes for the heart's electrical system to repolarize after a heartbeat. For women, understanding what constitutes a normal QTc is vital, as deviations can lead to serious health concerns. This article aims to provide in-depth knowledge about normal QTc for women, and how it can affect their overall well-being.
As we explore this topic, we will address common questions surrounding QTc, including how to measure it, the typical ranges for women, and how lifestyle factors and medical conditions can influence these values. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of normal QTc for women, empowering you to make informed decisions about your cardiovascular health.
Table of Contents
- What is QTc?
- Normal QTc Ranges for Women
- How is QTc Measured?
- Factors Affecting QTc Values
- Implications of Abnormal QTc
- Medical Conditions Related to QTc
- Lifestyle Factors Impacting QTc
- Conclusion
What is QTc?
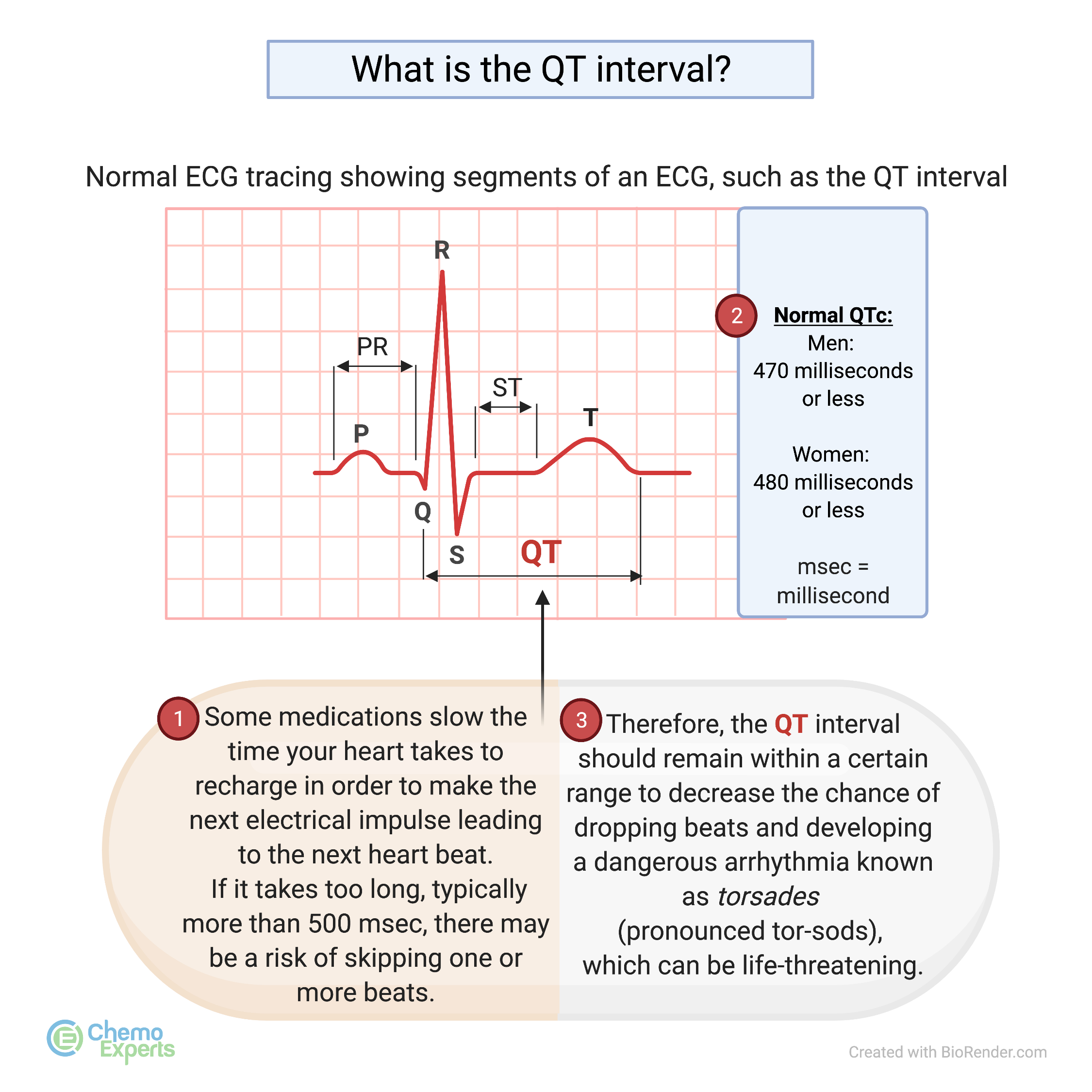
The QTc interval is a crucial measurement in electrocardiograms (ECGs) that reflects the time taken for the heart's ventricles to repolarize after contraction. Normal QTc values are essential for assessing cardiac function and identifying potential health issues. The 'c' in QTc stands for 'corrected,' indicating that the measurement has been adjusted for heart rate variations.
Understanding the Components of QTc
- QT Interval: The duration from the beginning of the Q wave to the end of the T wave on an ECG.
- Corrected QT (QTc): The QT interval adjusted for the heart rate, usually using the Bazett formula or other correction methods.
Normal QTc Ranges for Women
Understanding the normal QTc ranges for women is paramount for accurate diagnosis and treatment. Generally, a normal QTc interval for women is considered to be:
- Normal QTc: 350 to 460 milliseconds
- Borderline: 460 to 480 milliseconds
- Prolonged: Greater than 480 milliseconds
It is important to note that these values can vary based on individual health factors and the methodology used for measurement.
How is QTc Measured?
Measuring QTc involves obtaining an ECG recording, which provides the necessary data to calculate the interval. The following steps outline the measurement process:
- Obtain a 12-lead ECG to capture the heart's electrical activity.
- Identify the QT interval on the ECG tracing.
- Calculate the QTc using an appropriate formula, commonly the Bazett formula: QTc = QT / √(RR interval), where the RR interval is the time between two consecutive R waves.
Factors Affecting QTc Values
Various factors can influence QTc readings, resulting in variations among individuals. Some of these factors include:
- Age: QTc tends to increase with age.
- Sex: Women generally have longer QTc intervals compared to men.
- Medications: Certain drugs, particularly antiarrhythmics, can prolong the QTc interval.
- Electrolyte Imbalances: Levels of potassium, magnesium, and calcium can impact QTc.
Implications of Abnormal QTc
Abnormal QTc values can indicate various cardiac conditions, including:
- Increased Risk of Arrhythmias: Prolonged QTc may lead to life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias.
- Sudden Cardiac Death: Severe QTc prolongation has been associated with an increased risk of sudden cardiac events.
Medical Conditions Related to QTc
Several medical conditions can affect QTc intervals, including:
- Congenital Long QT Syndrome: A genetic condition that affects heart rhythm.
- Heart Disease: Conditions such as coronary artery disease can influence QTc.
- Hypothyroidism: This condition is often associated with prolonged QTc intervals.
Lifestyle Factors Impacting QTc
Certain lifestyle factors can also affect QTc readings, including:
- Diet: A diet low in potassium can prolong QTc.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity may help maintain a normal QTc interval.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can influence heart health and QTc intervals.
Conclusion
Understanding normal QTc for women is essential for maintaining heart health and preventing serious cardiac events. Regular monitoring of QTc intervals, awareness of risk factors, and lifestyle modifications can significantly contribute to overall cardiovascular well-being. If you have concerns about your QTc interval or heart health, consulting a healthcare professional is crucial.
We encourage readers to leave comments, share their experiences, and engage with our content. For more insightful articles about heart health and wellness, feel free to explore other sections of our site.
Thank you for taking the time to read this comprehensive guide on normal QTc for women. We hope to see you again soon!
Article Recommendations
- Dynamic Duo Roger Nores Amp Liam Holding Hands A Deep Dive
- Chadwick Bosemans Wife An Inspiring Love Story
- John Kincade Artist Inspiration