The linguistic diversity of the United States is a reflection of its rich cultural heritage and history. Languages spoken in America encompass a wide range of dialects and tongues, influenced by the myriad of immigrant communities that have settled in the country over the centuries. From the indigenous languages of Native American tribes to the languages brought by immigrants from all over the world, understanding the languages spoken in America is essential for appreciating the nation's cultural mosaic.
In this article, we will explore the various languages spoken in America, their origins, and their significance in contemporary society. We will delve into the statistics that highlight the linguistic landscape of the nation and discuss the impact of language on identity and community cohesion.
As we navigate through the fascinating world of languages in America, we will also consider the importance of language preservation and education, especially for minority languages that are at risk of fading away. Join us on this linguistic journey to uncover the languages that shape the American experience.
Table of Contents
- Overview of Languages Spoken in America
- Top Languages Spoken in America
- Indigenous Languages
- Language and Identity
- Language Preservation and Education
- Statistics on Language Use
- Conclusion
Overview of Languages Spoken in America
America is home to a vast array of languages, reflecting its status as a melting pot of cultures. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, approximately 21% of the population speaks a language other than English at home. This statistic underscores the country's linguistic diversity.
While English is the dominant language, other languages such as Spanish, Chinese, Tagalog, and Vietnamese have significant numbers of speakers. This multilingual environment is not only a testament to the nation's immigrant history but also shapes social interactions and community dynamics.
Top Languages Spoken in America
The following sections will examine the most widely spoken languages in America, highlighting their origins and cultural significance.
1. English
English is the most widely spoken language in the United States, with approximately 239 million speakers, making up about 78% of the population. The language has evolved significantly over the centuries, influenced by various linguistic and cultural shifts.
As the primary language of government, education, and media, English plays a crucial role in American society. Its global status has also made it an essential language for international business and diplomacy.
2. Spanish
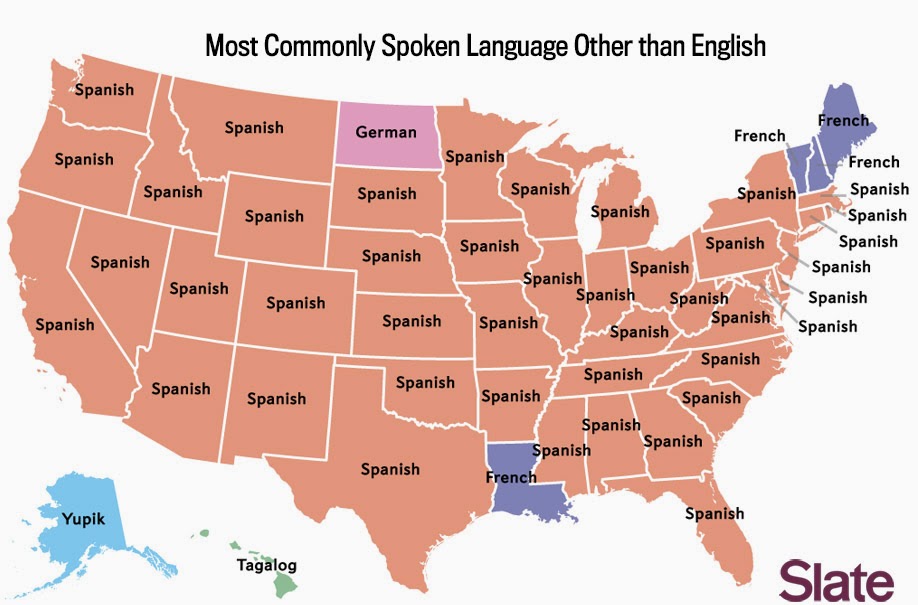
Spanish is the second most commonly spoken language in America, with around 41 million speakers, or 13% of the population. The presence of Spanish in the U.S. can be traced back to the early Spanish colonization of the Americas and has been further bolstered by immigration from Latin America.
Spanish is particularly prevalent in states such as California, Texas, and Florida, where large Hispanic communities reside. The growing influence of the Spanish language is evident in media, education, and public life.
3. Other Major Languages
In addition to English and Spanish, several other languages have significant numbers of speakers in America. These include:
- Chinese (Mandarin and Cantonese) - Approximately 3.5 million speakers.
- Tagalog - Over 1.7 million speakers, largely due to immigration from the Philippines.
- Vietnamese - Around 1.5 million speakers, primarily in communities with Vietnamese heritage.
- Arabic - Approximately 1.2 million speakers, reflecting the growing Arab-American population.
- French - About 1.2 million speakers, particularly in Louisiana and parts of New England.
Indigenous Languages
The linguistic landscape of America is also enriched by the presence of indigenous languages. There are over 175 different languages spoken by Native American tribes across the country. Some of the most notable indigenous languages include:
- Navajo - The most widely spoken Native American language in the U.S.
- Sioux - Spoken by several tribes in the Great Plains.
- Apache - A group of languages spoken by the Apache tribes.
Unfortunately, many of these languages are endangered due to historical suppression and the dominance of English. Efforts are underway to revitalize and preserve these languages through educational programs and community initiatives.
Language and Identity
Language is a powerful marker of identity, shaping how individuals see themselves and their communities. For many immigrants, maintaining their native language is crucial for cultural preservation and community cohesion. Language can foster a sense of belonging and provide a connection to one's heritage.
Moreover, bilingualism has been linked to cognitive benefits, enhanced communication skills, and greater cultural awareness. As such, promoting multilingualism in America can strengthen social bonds and enrich the national narrative.
Language Preservation and Education
Preserving linguistic diversity is essential for maintaining cultural heritage. Various organizations and initiatives are focused on promoting language education and revitalization, particularly for endangered languages. These efforts include:
- Language immersion programs in schools.
- Community language classes.
- Digital resources and online courses for self-study.
Additionally, advocacy for bilingual education can help ensure that future generations retain proficiency in both their native languages and English.
Statistics on Language Use
According to the most recent data from the U.S. Census Bureau, here are some key statistics on language use in America:
- Approximately 21% of the U.S. population speaks a language other than English at home.
- Spanish is the most common non-English language, spoken by 13% of the population.
- Other languages with significant speakers include Chinese, Tagalog, and Vietnamese.
- Over 175 indigenous languages are still spoken in the U.S., though many are endangered.
These statistics illustrate the vibrant linguistic tapestry of America and the importance of fostering a multilingual society.
Conclusion
In summary, the languages spoken in America reflect the country's rich cultural heritage and diverse immigrant experiences. English and Spanish dominate the linguistic landscape, but many other languages contribute to the nation's multicultural identity. Preserving and promoting linguistic diversity is essential for fostering community cohesion and cultural understanding.
We encourage readers to engage with their local communities, support language education initiatives, and explore the languages that enrich their lives. Share your thoughts in the comments below and consider reading more about the fascinating languages and cultures that make up America.
Thank you for joining us on this exploration of languages spoken in America. We hope to see you back here for more insightful articles on cultural diversity and heritage!
Article Recommendations
- Brad Pitt Angelina Jolies Former Husband
- Mark Calaways Impressive Net Worth Uncovering The Undertakers Financial Success
- Megan Fox Thanks Sharna Grateful For Dance Partner