Have you ever wondered about the nature of the Sun's movement in our galaxy? The question "does the sun have an orbit?" might seem simple, but it opens up a vast realm of astronomical concepts and discoveries. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of the Sun's motion, its relationship with other celestial bodies, and how it fits into the larger structure of our galaxy.
The Sun, at the center of our solar system, is not just a static ball of fire; it is a dynamic entity that participates in the grand dance of the Milky Way Galaxy. Understanding whether the Sun has an orbit involves delving into the physics of gravity, the structure of the galaxy, and how stars, including our Sun, move through space over time. As we embark on this journey, we will also touch on the implications of the Sun’s movement for life on Earth and our understanding of the universe.
In the following sections, we will analyze the concept of orbits in astronomy, the specific path of the Sun within the Milky Way, and the various forces that govern its motion. By the end of this article, you will have a clearer understanding of the Sun's orbit and its significance in the cosmos.
Table of Contents
- What is an Orbit?
- The Sun in the Solar System
- The Sun and the Milky Way
- How Does the Sun Move?
- Does the Sun Have an Orbit?
- Time to Complete an Orbit
- Effects on Earth
- Conclusion
What is an Orbit?
An orbit can be defined as the gravitationally curved trajectory of an object around a point in space. In our solar system, planets, moons, and even artificial satellites follow orbits primarily due to the gravitational pull from larger bodies like the Sun and Earth. Here are some key points about orbits:
- Orbits can be elliptical, circular, or parabolic.
- The shape and size of an orbit depend on the mass of the objects involved and their distance from each other.
- Newton's laws of motion and the law of universal gravitation are fundamental to understanding orbital mechanics.
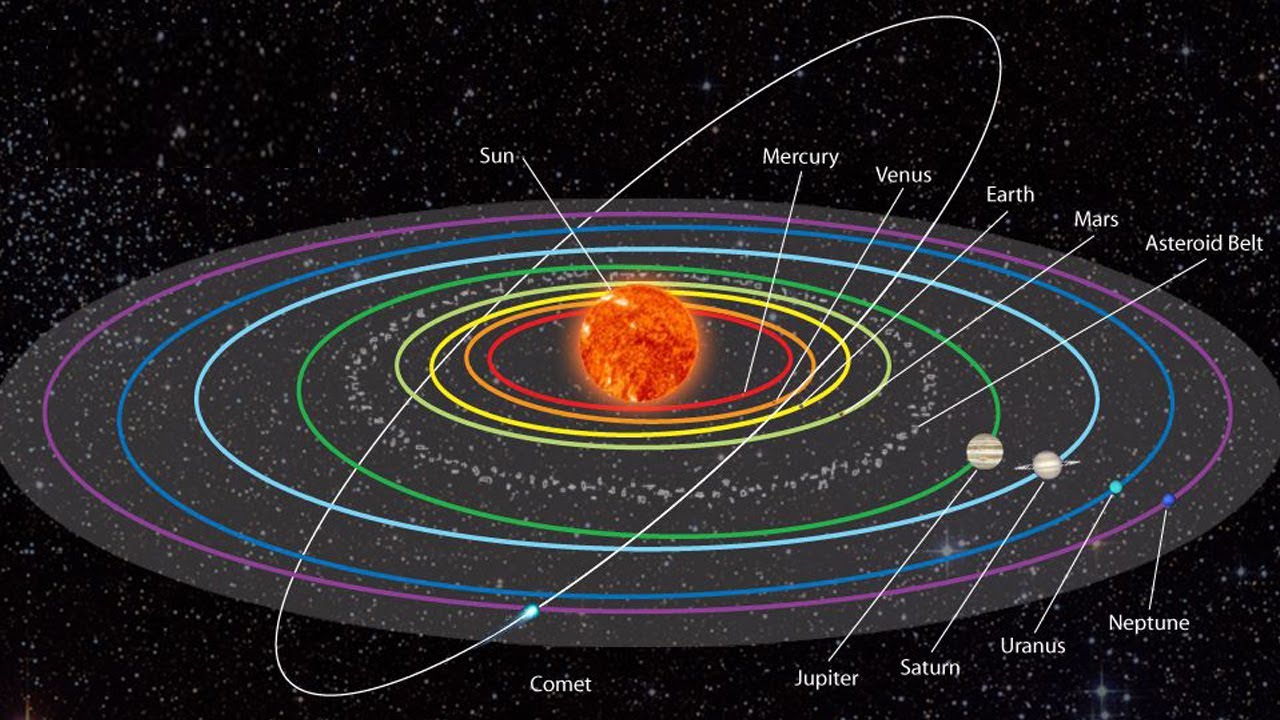
The Sun in the Solar System
The Sun is the central star of our solar system, around which eight planets, including Earth, orbit. It accounts for approximately 99.86% of the total mass of the solar system. Here are some interesting facts about the Sun:
- The Sun is composed mainly of hydrogen (about 74%) and helium (about 24%).
- It is approximately 4.6 billion years old.
- The diameter of the Sun is about 1.39 million kilometers.
The Sun and the Milky Way
Our solar system is situated in one of the spiral arms of the Milky Way Galaxy, known as the Orion Arm. The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy that is home to billions of stars, gas, dust, and dark matter. The structure of the Milky Way can be summarized as follows:
- It has a central bulge surrounded by a flat disk with spiral arms.
- There is a halo of dark matter surrounding the galaxy.
- The Milky Way is part of a local group of galaxies, which includes the Andromeda Galaxy.
How Does the Sun Move?
The Sun moves through space due to the gravitational forces exerted by other stars and celestial bodies in the galaxy. Its motion can be described as follows:
- The Sun orbits the center of the Milky Way galaxy.
- It moves at an average speed of about 828,000 kilometers per hour.
- The orbit is not a perfect circle but rather an elongated ellipse.
Does the Sun Have an Orbit?
Yes, the Sun does have an orbit. It orbits the center of the Milky Way galaxy, and this motion is a fundamental aspect of our understanding of cosmic dynamics. The Sun's orbit can be characterized by the following:
- The Sun takes about 225-250 million years to complete one orbit around the Milky Way's center, a journey often referred to as a "cosmic year."
- During its orbit, the Sun moves through regions with varying densities of stars, gas, and dust.
- The gravitational pull from nearby stars and the dark matter that permeates the galaxy influences the Sun’s path.
Time to Complete an Orbit
The time it takes for the Sun to complete one orbit around the Milky Way center is estimated to be between 225 to 250 million years. This long duration can be broken down into several interesting aspects:
- During this time, the solar system also moves through different regions of the galaxy that can affect conditions on Earth.
- This immense time scale helps scientists understand the evolution of the galaxy and its stars.
- Fossil records on Earth indicate that life has evolved through numerous cycles of the Sun’s orbit.
Effects on Earth
The Sun’s movement through the galaxy can have various effects on Earth, including:
- Changes in cosmic radiation exposure as the solar system moves through different regions of the galaxy.
- Potential influences on the solar activity cycle, which can affect climate and weather patterns.
- Interactions with other stars and stellar phenomena that may have implications for life on Earth.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Sun does indeed have an orbit, and it plays a crucial role in the dynamics of the Milky Way galaxy. Understanding the Sun's movement helps us appreciate the cosmic forces at play and their potential impacts on our planet. If you found this article informative, consider leaving a comment or sharing it with others interested in astronomy. For more intriguing topics, feel free to explore our other articles.
We hope this exploration of the Sun's orbit has sparked your curiosity about our universe. Stay tuned for more fascinating insights!
Article Recommendations
- Megan Fox Baby Daddy Video Shocking Details Revealed
- Buscar Kid And His Mom Cctv Video Original A Detailed Insight
- Don Galloways Financial Overview Net Worth Analysis And More