Substitution cryptography is a fascinating area of study that combines elements of mystery and mathematics. This cryptographic method replaces elements of the plaintext with corresponding elements of the ciphertext, creating a coded message that can only be deciphered by those who possess the key. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of substitution cryptography, its historical significance, modern applications, and methods for decoding messages. Whether you are a beginner or an expert in the field of cryptography, this guide will provide valuable insights.
The history of cryptography dates back thousands of years, with substitution ciphers being among the earliest forms of encryption. From the simple Caesar cipher used by Julius Caesar to complex modern algorithms, substitution cryptography has evolved yet remains grounded in its fundamental principles. Understanding how to decode these ciphers is essential for anyone interested in cryptography, cybersecurity, or even just solving puzzles.
As we delve into the world of substitution cryptography, we will examine various types of substitution ciphers, techniques for decoding them, and the tools available for cryptographic analysis. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of substitution cryptography and be equipped with the knowledge to decode messages effectively.
Table of Contents
- What is Substitution Cryptography?
- History of Substitution Cryptography
- Types of Substitution Ciphers
- How to Decode Substitution Ciphers
- Tools for Decoding Substitution Ciphers
- Applications of Substitution Cryptography
- Challenges in Substitution Cryptography
- Future of Substitution Cryptography
What is Substitution Cryptography?
Substitution cryptography is a method of encryption where each letter in the plaintext is replaced with a letter from a fixed substitution alphabet. This can be a simple transformation, where each letter is shifted by a certain number of places in the alphabet, or can involve a more complex algorithm that uses a randomly shuffled alphabet. The key to decoding the message lies in knowing the substitution rules.
How Does Substitution Cryptography Work?
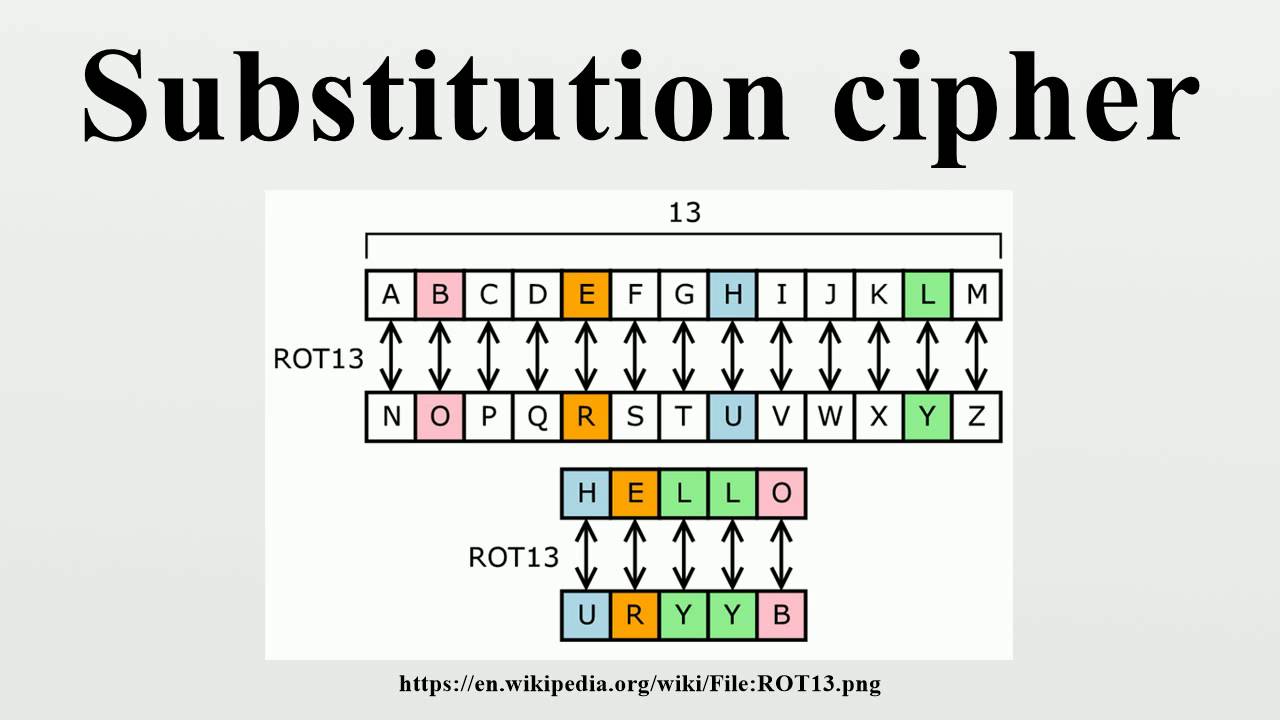
The basic principle of substitution cryptography involves two main components: the plaintext and the ciphertext. The plaintext is the original message, while the ciphertext is the transformed message after applying the substitution rules. For example, using a Caesar cipher with a shift of three, the letter 'A' would be replaced with 'D', 'B' with 'E', and so on. The decoding process involves reversing this transformation to retrieve the original message.
History of Substitution Cryptography
The use of substitution ciphers dates back to ancient civilizations. One of the earliest known examples is the Caesar cipher, named after Julius Caesar, who reportedly used it to communicate with his generals. Throughout history, substitution ciphers have played a crucial role in military communication and espionage.
Types of Substitution Ciphers
There are several types of substitution ciphers, each with unique characteristics:
- Simple Substitution Cipher: Each letter of the alphabet is replaced with another letter.
- Homophonic Substitution Cipher: Each letter can be replaced by multiple symbols, making frequency analysis more challenging.
- Polygraphic Substitution Cipher: Groups of letters are substituted instead of individual letters, increasing complexity.
- Caesar Cipher: A specific type of simple substitution cipher that shifts letters by a fixed number of places.
How to Decode Substitution Ciphers
Decoding substitution ciphers can be accomplished through various methods:
Frequency Analysis
One of the most effective techniques for decoding substitution ciphers is frequency analysis. This method involves analyzing the frequency of letters in the ciphertext and comparing them to the typical letter frequencies in the target language. For example, in English, the letter 'E' is the most frequently used letter, followed by 'T', 'A', and so on. By identifying common letters, a decoder can make educated guesses about the substitutions used.
Pattern Recognition
Another method is pattern recognition, where the decoder looks for patterns in the ciphertext that correspond to common words or phrases. For instance, single letters are often 'A' or 'I', while common two-letter words include 'HE', 'TO', and 'OF'. Recognizing these patterns can provide critical clues for decoding the message.
Tools for Decoding Substitution Ciphers
In the digital age, various tools and software are available to assist in decoding substitution ciphers:
- CrypTool: An educational tool for learning about and practicing cryptography.
- Online Cipher Decoders: Websites that offer automated decoding of substitution ciphers.
- Manual Decoding Techniques: Using pen and paper to apply frequency analysis and pattern recognition methods.
Applications of Substitution Cryptography
Substitution cryptography has numerous applications in various fields:
- Data Security: Used to protect sensitive information in digital communications.
- Puzzle Solving: Popular in cryptographic puzzles and escape rooms.
- Historical Research: Analyzing historical texts that utilize cryptographic techniques.
Challenges in Substitution Cryptography
Despite its utility, substitution cryptography faces several challenges:
- Vulnerability to Frequency Analysis: Simple substitution ciphers are susceptible to frequency analysis, making them easier to break.
- Advancements in Cryptography: Modern encryption methods, such as symmetric and asymmetric encryption, offer enhanced security.
Future of Substitution Cryptography
The future of substitution cryptography lies in its integration with modern encryption techniques. As technology advances, hybrid methods that combine traditional substitution with more robust algorithms may emerge, providing stronger security while maintaining the simplicity of substitution ciphers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, substitution cryptography is a timeless method of encoding messages that has evolved from ancient times to the present day. By understanding its principles, types, and decoding techniques, you can appreciate both the art and science behind cryptography. We encourage you to explore further, experiment with decoding, and share your insights in the comments below!
Final Thoughts
Thank you for reading this comprehensive guide on substitution cryptography. We hope you found the information valuable and informative. Be sure to visit our site for more articles on cryptography and related topics. We look forward to seeing you again!
Article Recommendations
- Megan Foxs Natural Eye Color Stunning Shades
- The Perfect Heartfelt Birthday Wishes For A Cherished Friend
- Did Melania Trumps Sister Skip Her Mothers Funeral